The classification of fiber optics products within the Harmonized System (HS) Codes presents a unique set of challenges that stem from several key factors. These obstacles not only require a detailed understanding of the product itself but also a keen awareness of the constantly evolving landscape of technology and international trade regulations. Below, we delve into these challenges more deeply, outlining the specific hurdles and offering insights on how to navigate them.
Rapid Technological Advancements
The field of fiber optics is at the forefront of technological innovation, with new products and applications being developed at a swift pace. This rapid evolution can lead to discrepancies between the existing HS Code framework, which is updated periodically, and the latest products on the market. As a result, businesses and customs authorities may struggle to find a direct match for the newest fiber optics products within the current HS Code classifications. Staying abreast of the latest developments in fiber optics technology and anticipating potential classification challenges are crucial steps in mitigating this issue.
Schedule B codes
For American exporters, the Schedule B code is a 10-digit subset of HTS codes. It must be mentioned on all documents or filings used exclusively for export. The US government tracks US exports using Schedule B codes for statistical purposes.
Schedule B codes are maintained by the U.S. Census Bureau instead of the International Trade Commission.
The first six digits of a Schedule B code, like HTS codes, should match those of an HS number. However, the last four digits of a Schedule B code may differ even from the HTS code, making it easier to accurately identify and classify products.
Difference between HS, Schedule B and HTS codes
After reading about these three codes, it’s easier to become confused as to which code you should choose while shipping your goods.
Take a look at the table below to understand the difference between them.
|
Difference between HS, Schedule B and HTS codes
|
|
Number of digits |
Import or export |
Governing authority |
When they’re used |
| HS Codes |
6 |
Global use |
World Customs Organization |
Used to reference classification with anyone outside the US |
| HTS Codes |
10 |
US import |
U.S. International Trade Commission |
Specific to the US and must be used by US importers. HTS codes are not recognized globally |
| Schedule B Codes |
10 |
US export |
U.S. Census Bureau |
They’re a subset of HTS codes. Companies that export from the US usually use these codes because certain HTS codes can’t be used for exports |
Functions of HTS codes
HTS codes have several functions in international trade. For starters, these codes help government officials identify the goods that are being imported or exported across US borders. HTS codes also enable officials to apply appropriate taxes for various product categories.
Besides being a vital tool for customs clearance, HTS codes classify and categorize products in a worldwide system. The US government and the international trading sector report and analyze the trade data using HTS codes. These codes give them insights into the inflow, import quotas, outflow, tax revenue, and domestic production of specific goods. This supports the US government and the international trading sector to make better policies to improve their international trade.
Being part of the shipping industry, it’s your responsibility to make sure your cargo has the right product classification code. Otherwise, your cargo may get stuck in the port and you may end up paying late fees like demurrage or detention or other port charges. Read on to find out how you can identify your product’s HTS code.
How do you identify your product’s HTS code?
Identifying your cargo’s HTS code is crucial. You can easily look up your product’s HTS code by using ITC’s free search tool here:

If you want to find out the Schedule B code for your cargo, then use the Census Bureau Search tool:

How to use HTS code to identify import duty
As we mentioned before, HTS codes also help you identify how much import duty you’ll have to pay. This can help you plan your logistics better and calculate the cost of shipping.
If you are importing from a country that has entered into an international trade agreement with the US, then the US customs duty rates on a particular commodity are likely to be reduced. However, this discount does not apply to all products. You can obtain detailed information about this by checking the official HTS list published by the United States International Trade Commission.
Specialized Nature of Products
Fiber optics products are inherently specialized, often designed for specific applications within telecommunications, medical devices, or industrial equipment. This specialization means that a one-size-fits-all approach to classification is ineffective. For instance, the same type of optical fiber could be classified differently depending on whether it's intended for use in medical imaging equipment or for broadband internet infrastructure. Understanding the intended use and the specific features of a product is essential for accurate classification under the HS Codes.
Detailed Technical Specifications
The precise classification of fiber optics products frequently hinges on their detailed technical specifications. Factors such as the wavelength of light the fiber is designed to carry, its mode (single-mode or multimode), and its protective coating or casing can all influence the correct HS Code. For businesses, providing comprehensive technical documentation to customs authorities can facilitate the correct classification and prevent delays in shipping or additional duties.
Integration into Larger Systems
Many fiber optics products are components of larger systems, and their classification can depend on the context of their use within these systems. For example, an optical fiber used in a medical endoscope might be classified under a different code than one used in a telecommunications network, even if the fibers themselves are similar. Understanding the broader system in which a fiber optics product is used can be critical for determining the most appropriate HS Code.
Navigating these challenges requires a collaborative effort between manufacturers, exporters, customs brokers, and classification experts. Keeping detailed records of product specifications, maintaining open lines of communication with customs authorities, and staying informed about changes to the HS Code system are all strategies that can improve the accuracy of fiber optics product classification. Additionally, leveraging the expertise of classification specialists or consulting with the World Customs Organization can provide valuable guidance in complex or ambiguous cases.
In summary, the classification of fiber optics products under HS Codes is a nuanced process influenced by the product's technical characteristics, intended use, and the context of its application. By understanding these challenges and adopting a proactive approach to classification, businesses can navigate the complexities of international trade more effectively, ensuring compliance and facilitating the smooth movement of goods across borders.
Optimizing Global Trade: Navigating Tariffs on Optical Fiber Cables for a Competitive Edge
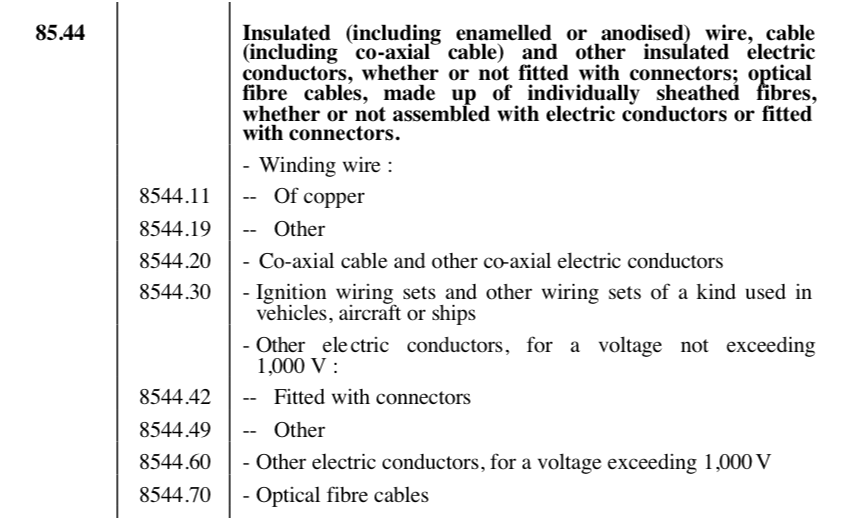
In an effort to keep our valued clients informed on matters affecting the industry, we'd like to share insights on the current tariff situation for optical fiber cables classified under HS code 8544.70.00.00. In the United States, these products are subject to a general duty rate of "Free," meaning no duty is applied under general conditions. However, it's crucial to note that products originating from specific countries, such as Cuba and North Korea, face a significantly higher rate of 65%. Moreover, optical fiber cables produced in China are subjected to an additional duty, which is the standard rate plus a 25% tariff due to trade measures imposed on Chinese goods.
This information is particularly relevant in the context of ongoing global trade dynamics and underscores the importance of understanding the source and classification of products. For Beyondtech and our clientele, the focus on European-made products offers a strategic advantage, circumventing the complexities and additional costs associated with tariffs on products from certain countries.
For those seeking further details, the HTS (Harmonized Tariff Schedule) provides comprehensive guidance on tariff rates and classifications for all merchandise imported into the United States. It's a valuable resource for companies navigating the import process and looking to optimize their trade strategies.
Disclaimer
This article provides a general guide to the HS Codes associated with fiber optics products. Given the complexity and specificity of HS Code classification, it is advised to consult with customs experts or relevant authorities for definitive classification. The codes mentioned here are based on a general understanding and may be subject to changes or revisions by the World Customs Organization or individual country customs authorities.
In summary, the correct classification of fiber optics products is essential for ensuring compliance with international trade regulations. By understanding the relevant HS Codes and the criteria for their application, businesses can navigate the complexities of trade more effectively.