Selecting between Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a Ethernet cables
In the market of technology, there are thousands of cables available that you can buy to make your network connection better and faster.
The most commonly are Ethernet cables Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6 and Cat6a.
As you may guess by now, there is a subtle difference between them.
But first:
What’s an Ethernet cable?
Ethernet cables emerged as a protocol to cover the needs of access to the local area network, but since 2001 they have expanded and their popularity has increased.
Currently, Ethernet cables are commonly used to interconnect the majority of technology devices at home or in the office.
Exist different types of these cables, they change and improve with time, and the most widely used now are the Cat5e, and Cat6.
But, which one is better?
Well, let's find out which are the benefits and disadvantages of each cable, so you can select the most appropriate for your network.

Key factors to differentiate Cat5e, Cat6, and others
If you are looking for differences to make comparisons between wires, there are three factors you need to keep in mind:
-
Speed of transmission
The speed of transmission changes according to the category.
It depends of the time the cable takes to transport data from one point to another and is measured in Megabits per second (Mb/s) or Gigabits (Gb/s) per second.
The speed of transmission is one of the most important characteristics to keep in mind because it determinate the effectiveness of the cable.
-
Bandwidth
The bandwidth refers to the cable's rate of data transmission.
When network bandwidth increases, information transmission is faster.
The bandwidth is measured in a unit of frequency called Megahertz, if a cable has a higher frequency of MHz, the transmission speed is more efficient.
-
Crosstalk reduction
Crosstalk is a perturbation of the communication network.
Is produced when many cables are together and the circuit's signal is perturbed due to the electromagnetic fields produced by other cables.
The consequences are interference, information loss, and failures in data security.
But this interference can be reduced using different methods, in this case, we will consider two different physical techniques that reduce the crosstalk.
- The first method is the internal twist of the wires and the differences of lengths between each type of cable.
This aspect is not a regulated feature and all companies are free to do it as they prefer, is recommended to acquire cables with more twists because the crosstalk is lower.
- The other key factor is the thickness of the sheath. With a wider thick the external crosstalk penetrates less in the circuit.
Some cables include a nylon spline to reduce crosstalk, but this is not common and is only used in cables that don't reach the standard regulations.

Cat5, an obsolete option
This cable used to be the most popular but now is considered obsolete because the newest versions of Ethernet cables have improved their quality.
Its speed of transmission ranges between 10 and 100 Mb/s, and rate of transmission is 100 Mhz.
In order to reduce crosstalk, Cat5 cables use typical methods.
These cables are twisted in longitudes of less than 1.5 - 2 twist per centimeter, which is considered too little and not efficient at all.
Usually, Cat5 cable’s sheath's thickness allows reducing crosstalk, which is a positive aspect.
Cat5e, the popular cable
Currently, this is the most used Ethernet cable on the market, the "e" on the name is an acronym for enhanced.
Cat5e is an improved version of Cat5.
It is considered the most efficient option because is not expensive and has a speed of transmission of 1 Gb/s and 100 MHz.
As if that’s not enough, the internal interference is lower, because the cable has an average of two twists per centimeter, which allow to transmit data without significant signal degradation.
For all those reasons, Cat5e is one of the best sellers Ethernet cables
Cat6, the future of connections
This is one of the latest actualization of Ethernet cables.
Cat6 has a range of transmission speed between 1 and 10 Gb/s.
Bandwidth is also superior, with 250 Mhz, a great improvement when compared to lower categories.
Something amazing about this version is that it is compatible with systems that use Cat5 or Cat5e cables.
But that’s just part of the story, Cat6 also is covered with a special thick sheath made of plastic that reduces crosstalk.
Internally, these cables have more than two twists per centimeter, which is a fantastic upgrade because it helps to reduce the internal interference of the circuits significantly.
Cat6 cables are a little more expensive than Cat5e cables, so they are recommended to be used in offices or companies that need very fast data transmission.
Of course if you are a fan of technological improvements this is for you because it is one step closer to the future.
Cat6a, a fancy improvement
This version of Ethernet cable represents the upcoming of this type of connection.
The "a" means augmented, because it is an actualization of the wire, with some details upgraded compared to the last version.
The speed of transmission is 10 Gb/s, the same range as Cat6, but with a better capability.
However, this cable's big improvement is the 500 MHz bandwidth.
Physically, the thickness and the twists of the wires is pretty much the same than the Cat6.
Cost isn't that much higher compared with the older version and the benefits that Cat6a offers are meaningful.

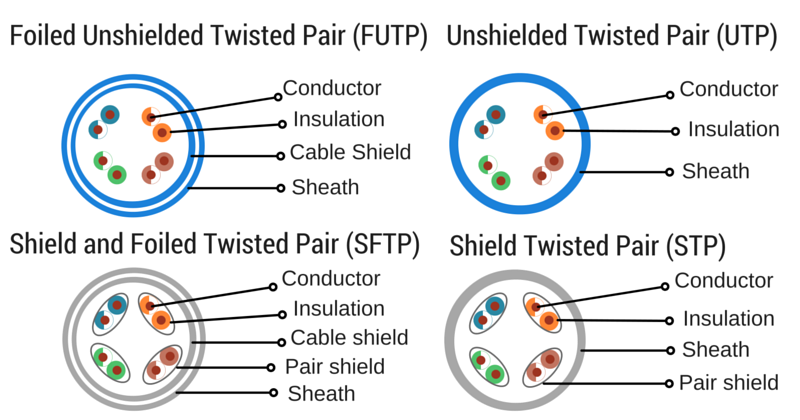
Differences between UTP and STP
Ethernet cables also have another difference and is that the internal wires that integrate the cable can be UTP or STP.
Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) means the internal wires are, you guessed, unshielded.
They are more sensitive to interference and suitable for connections inside a room or for short distances, but not recommended for exteriors or places where devices are too separated from each other.
On the other hand, shield twisted pair (STP) cables have internal shields between the wires.
This mean is less probably to be affected for crosstalk, that’s why they are the best option for long distances and outdoors.
Are you asking yourself how these shields work? It’s easy!
The process consists of an insulated material surrounding each of the internal pairs of wires inside of the Ethernet cables.
This prevents the circuits to produce internal crosstalk, avoiding the loss of data and reducing the interference of electromagnetic fields.
Solid or stranded cables?
This is another feature to consider before acquiring an Ethernet cable.
In this case, the difference is the internal copper structure conductor inside the wires.
When the cable is solid, it means it uses a single copper wire to transmit information.
This version is recommended for permanent installations, such as walls or floors. Solid cables are more durable than stranded cables, but not that flexible.
The other type is stranded cables.
In this case, the copper structure is made of many pieces of copper wires twisted together.
This version is more flexible than solid, so is perfect to close connections in places with a lot of movement, but is not so durable.
Can I use the same plugs to Cat5e and Cat6?
Well, this is a tricky question!
When you are in the process of changing Cat5e cables for a new version of Ethernet cables you have to decide if also changing the cables plugs of the cables or not.
If you make a quick research, most of blogs will tell you that is a good idea to use the same plugs for both versions.
The truth is that Cat6 cables have a slightly large diameter than Cat5e cables, so even if they look the same, they are not.
You can use the plugs designed for Cat5e to connect the Cat6 for a short period of time.
But in the future, you will notice connection problems, like the a loss in transmission speed or an increase in the crosstalk.
If you do this you will not be taking advantage of all the potential that Cat6 can offer and will end up being the same as a Cat5e cable.
Considering this, our recommendation is to invest some money and change old RJ45 plugs for newer RJ45 versions specially designed for Cat6 cables, so you can enjoy all the benefits of your new improved network connection.
You should also keep in mind that there are several differences between the design of solid or stranded cables' plugs.
Therefore, before buying plugs, you should know which type of cable you are using.

So which one should you use?
Now that you have complete knowledge of the differences between cables, this question must be popping in your head.
Considering all the aspects that we already mentioned, we suggest you choose between the Cat5e and Cat6, why?
Simply, because these are the options that will give you more benefits with a lower cost.
Our recommendation is:
If you have an office where you need to transfer files between computers quickly, go for Cat6 cables, they are just better.
But if your goal is to increase the internet speed, both cables will suit your needs.
Remember that the Internet speed depends not only on the types of cables that you use, but also that the router and the computer card have the gigabit capacity.
We invite you to try to acquire shield cables because these are better reducing the interference on the internal structure, which can make a significantly difference avoiding the data loss increasing the speed of data transmission.
When it comes to costs, the difference between Cat5e and Cat6 is little.
In general, Cat6 cables are 10% to 20% more expensive than Cat5e cables.
It is important that you always buy cables from a trustful provider. That way, you can be sure they have good quality.
We hope after reading this, you can easily choose a cable that suits your needs.